Wednesday, 3 October 2012
Data manipulation
Data manipulation
Hilbert and Lopez identify the exponential pace of technological change. Machines application specific capacity to computers information per capita roughly doubled every 14 months between 1986 and 2007 the per capacity of the world's general-purpose computers doubled every 18 months during the same two decades. The global telecommunication capacity per capita doubled every 34 months.The world's storage capacity per capita required roughly 39 to 40 months to double (every 3 years and per capita broadcast information has doubled every 12 years.
Massive amounts of data stored worldwide every day unless it can be analysed presented effectively it essentially resides in what have been called data tombs data archives that are seldom visited. To address that issue, the field of data mining which can be defined as the process of discovering interesting patterns and knowledge from large amounts of data emerged in the late 1980's.
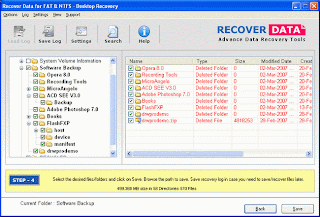
Data retrieval
Data retrieval
Database model introduced a programming language independent Structured Query Language "SQL" based on relational algebra.
"Data" and information are not synonymous. Anything stored is data but it only becomes information when it is organised and presented meaningfully. Most of the world's digital data is unstructured and stored in a variety of different physical formats within a single organisation.
"Data" warehouses began to be developed
in the 1980's to integrate these disparate stores.Typically contain
data extracted from various sources including external sources such as Internet organised in such way as to facilitate decision support
systems.
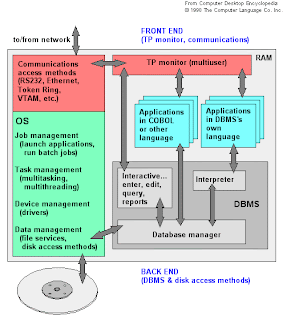
Database management system
Database management system
All database management systems
consist of a number of components that together allow the data they
store to be accessed simultaneously by many users while maintaining its
integrity. A characteristic of all databases is that the structure of
the data they contain is defined and stored separately from data
itself in database schema.
Database management systems emerged to address the problem of storing and retrieving large amounts
of data accurately and quickly. One of the earliest such systems was
IBM Information Management System. which is still widely
deployed more than 40 years later. IMS stores data hierarchically. The first commercially available relational
database management system was available from Oracle in 1980.
The extensible markup language
has become a popular format for data representation in recent years.
Although XML data can be stored in normal file systems, it is commonly
held in relational databases to take advantage of robust
implementation verified by both theoretical and practical
effort As an evolution of the Standard Generalized Markup Language
(SGML), XML's text based structure offers advantage of being both
machine and human readable.
Data storage device
Data storage device
Most digital data today is still stored
magnetically on devices such as hard disk drives, or optically on media. It has been estimated that the worldwide capacity to
store information on electronic devices grew from less than 3 exabytes
in 1986 to 295 exabytes in 2007.Doubling roughly every 3 years.
Early
electronic computers such as Colossus made use of punched tape a long
strip of paper on which data was represented by a series of holes, a
technology now obsolete. Electronic data storage used in modern
computers dates when a form of delay line
memory was developed to remove the clutter from radar signals the first
practical application of which was the mercury delay line. The first
random access digital storage device was the Williams tube, based on a
standard cathode ray tube.The information stored in it and delay
line memory was volatile in that it had to be continuously refreshed
and thus was lost once power was removed. The earliest form of
non volatile computer storage was the magnetic drum invented in 1932 and
used in the Ferranti Mark 1.The world's first commercially available
general purpose electronic computer.
History of computing hardware
History of computing hardware
Devices been used to aid computation for thousands of years probably initially in the form of a tally stick.Comparable geared devices did not emerge in Europe until the 16th century, and it was not until 1645 that the first mechanical calculator capable of performing the four basic arithmetical operations was developed.The Antikythera mechanism, dating from about the beginning of the first century BC, is generally considered to be the earliest known mechanical analog computer.The earliest known geared mechanism. The electromechanical Zuse completed in 1941, was the world's first programmable computer.Colossus developed during the Second World War to decrypt German messages was the first electronic digital computer but although programmable it was not general purpose being designed for a single task. Neither did it store its programs in memory programming was carried out using plugs and switches to alter the internal wiring.Electronic computers using began to appear in the early 1940s.
Devices been used to aid computation for thousands of years probably initially in the form of a tally stick.Comparable geared devices did not emerge in Europe until the 16th century, and it was not until 1645 that the first mechanical calculator capable of performing the four basic arithmetical operations was developed.The Antikythera mechanism, dating from about the beginning of the first century BC, is generally considered to be the earliest known mechanical analog computer.The earliest known geared mechanism. The electromechanical Zuse completed in 1941, was the world's first programmable computer.Colossus developed during the Second World War to decrypt German messages was the first electronic digital computer but although programmable it was not general purpose being designed for a single task. Neither did it store its programs in memory programming was carried out using plugs and switches to alter the internal wiring.Electronic computers using began to appear in the early 1940s.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)